The Basics of Electrical Panels
What is an Electrical Panel?
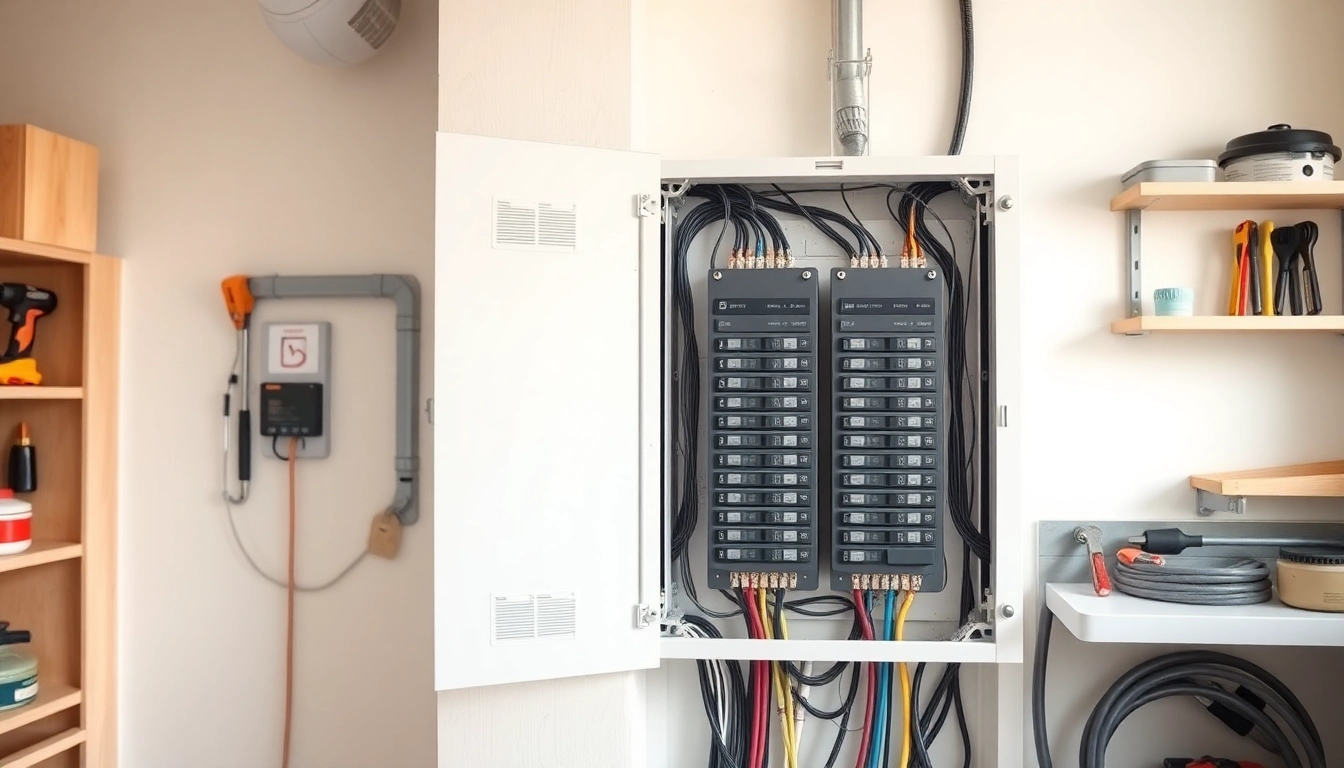
An electrical panel, sometimes referred to as a breaker box or fuse box, is a crucial component of your home’s electrical system. It serves as the central hub where electricity from the utility company enters the home and is distributed to various circuits throughout your residence. Essentially, an electrical panel manages the flow of electricity to your appliances and outlets, ensuring that each part of your home receives the power it requires to operate efficiently and safely.
Key Components of an Electrical Panel
Understanding the key components of an electrical panel can help homeowners identify its functions and the importance of each part. Some of the main components include:
- Main Breaker: This is the switch that controls the entire electrical system in your home. It can cut off power to all circuits for maintenance or emergencies.
- Circuit Breakers: These are switches that protect individual circuits from overloads. If too much current flows through a circuit, the breaker will trip, preventing potential hazards.
- Neutral Bus Bar: This bar connects all neutral wires from circuits, ensuring a path for the return current.
- Grounding Bus Bar: This safety feature is essential in preventing electrical shocks, directing harmful electricity to the ground.
- Enclosure: The outer case that protects the components inside from dust, animals, and accidental contact.
Understanding Main Breaker vs. Subpanels
Understanding the differences between main breakers and subpanels is important for homeowners assessing their electrical needs. The main breaker is the primary switch that controls all electrical circuits within the home, usually located at the main electrical panel. In contrast, subpanels are extensions of the main panel; they are smaller panels that distribute power to specific areas of the house. They are beneficial when electrical demand exceeds the main panel’s capacity or when circuits need to be organized more efficiently.
Signs You Need to Upgrade Your Electrical Panel
Common Warning Signs to Watch For
Recognizing the signs that it may be time to upgrade your electrical panel can help prevent safety issues and ensure that your home’s electrical system runs smoothly. Some common warning signs include:
- Frequent Tripping: If your circuit breakers trip often, this is a sign that your panel may not handle your electrical load efficiently.
- Flickering Lights: Lights that flicker or dim when larger appliances turn on can indicate problems with your electrical panel or wiring.
- Burning Smells: Any burning smells coming from the panel are a huge red flag and should be addressed immediately as this may lead to a fire hazard.
- Buzzing Sounds: Unusual buzzing sounds may point to faulty breakers or poor connections.
How Lifestyle Changes Affect Your Electrical Needs
Changes in lifestyle significantly impact your electrical requirements. If you’ve recently added new electronic devices, remodeled your home, or increased the number of occupants, your current electrical panel may not be sufficient. It’s crucial to evaluate your electrical consumption regularly, especially when significant upgrades, like home appliances or smart home systems, are introduced.
Age Considerations for Electrical Panels
Most electrical panels have a lifespan of about 25 to 40 years. If your panel is aging, it may be outdated and unable to meet modern power demands safely. Panels manufactured before the 1980s are particularly prone to safety issues, and if your home has such a panel, it is wise to consider an upgrade to comply with current safety standards.
Choosing the Right Electrical Panel for Your Home
Assessing Your Power Needs
To choose the right electrical panel, begin by assessing your power consumption needs. Consider the total wattage of all your electrical devices, lighting fixtures, and any new technologies you plan to incorporate into your home. A standard residential panel often provides between 100-200 amps; however, larger homes or those with high electrical usage may benefit from panels with even greater capacity.
Types of Electrical Panels Available
There are various types of electrical panels available to suit different home sizes and electrical needs. The main categories include:
- Main Breaker Panel: This is the most common type in residential settings, controlling the entire electrical distribution.
- Subpanel: As previously mentioned, these are used to extend the system, often installed in areas with high electrical demand.
- Smart Panels: These modern panels come equipped with advanced technology that enables homeowners to monitor and manage energy usage through mobile apps.
- Load Centers: These systems provide flexibility, allowing for future expansions and additional circuits.
Cost Factors for Electrical Panel Installation
The cost of installing a new electrical panel varies based on several factors including:
- Type and Size: Higher capacity panels generally cost more.
- Labor Costs: Hiring a licensed electrician ensures safety and compliance with local codes, so labor costs can significantly impact the total price.
- Location: Installation difficulty can vary by the layout of the home, with accessibility impacting labor time and costs.
- Additional Materials: If upgrading electrical wiring, additional costs for cables and other materials must be considered.
Electrical Panel Maintenance Tips
Regular Inspections and Professional Help
Regular inspections by a qualified electrician are critical in ensuring your electrical panel functions correctly and safely. It’s advisable to schedule these inspections every three to five years. During inspections, electricians check for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage within the panel that might indicate potential issues.
How to Clean and Maintain Your Electrical Panel
Maintaining your electrical panel is crucial for safe operation. Homeowners should ensure that the area around the panel is clean and free from dust or any flammable materials. Periodic cleaning can be performed; however, ensure that the power is off before attempting to clean any part of the panel to avoid electrical shocks.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Identifying and rectifying minor issues can save you from more significant problems down the line. Some common troubleshooting actions include:
- Checking Breakers: If a breaker keeps tripping, identify which circuit is causing the issue and reduce the load on that circuit.
- Inspecting Connections: Ensure that connections are tight and secure, as loose connections can lead to power fluctuations or electrical fires.
- Monitoring for Overheating: If the panel or wires feel hot to the touch, it may indicate an overload, requiring immediate attention.
Conclusion: Making Informed Decisions About Your Electrical System
Planning for Future Upgrades
As technology evolves and power needs increase, planning for future upgrades becomes essential. Consider your current and anticipated electrical consumption as you make holistic decisions about your electrical panel and wiring systems.
The Importance of Professional Consultations
Consulting with a licensed electrician can provide invaluable insights into your specific electrical needs. Professional help ensures that decisions made about upgrading or maintaining your electrical panel are safe, compliant, and tailored to your home.
Keeping Safety as Your Top Priority
Safety should always be at the forefront when dealing with your electrical system. Understanding your electrical panel and recognizing when to seek upgrades or professional assistance can safeguard your home from potential electrical hazards.